Unveiling the Power of Manganato: A Versatile Compound with Remarkable Applications

Introduction
The world of chemistry is a realm of constant exploration and discovery, and the compound known as manganato” stands as a testament to the remarkable versatility and potential hidden within the periodic table. Manganato is a compound of manganese, an essential transition metal, and oxygen, a fundamental element of life. In this article, we will delve into the intriguing world of manganato, uncovering its structure, properties, and a multitude of applications that make it a pivotal player in various fields of science and technology.
Manganato: Decoding the Structure
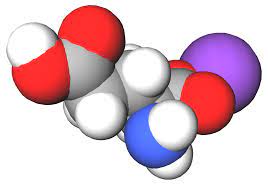
Manganato’s chemical formula is MnO4-. This means it is composed of one manganese atom (Mn) and four oxygen atoms (O). The minus sign indicates that it is an anion, or a negatively charged ion. The distinctive tetrahedral structure of the manganato ion is central to its unique properties and reactivity. Its molecular arrangement allows for fascinating interactions with other substances, leading to a wide array of chemical reactions.
Exceptional Properties of Manganato
Manganato is known for its remarkable properties, including
Vibrant Color: Manganato compounds are often vividly colored, with a characteristic purple or dark green hue, making them easy to identify in various chemical reactions.
Oxidizing Agent: Manganato ions are potent oxidizing agents, readily accepting electrons from other substances in chemical reactions. This property makes them valuable in analytical chemistry and many redox reactions.
Solubility: Manganato compounds are typically soluble in water, further expanding their utility in aqueous solutions and industrial processes.
Stability: Manganato compounds are stable under various conditions, making them suitable for long-term storage and use.
Applications of Manganato
Manganato’s versatility extends to a wide range of applications in science and industry. Some notable uses include:
Analytical Chemistry: Manganato is a crucial reagent in titration, a widely used method for quantitative analysis in chemistry. Its powerful oxidizing properties enable the precise determination of the concentration of various substances, including organic compounds and ions.
Water Treatment: Manganato is employed in water treatment processes to remove contaminants, such as iron and hydrogen sulfide, by oxidizing them and facilitating their precipitation and removal.
Organic Synthesis: Manganato plays a vital role in the synthesis of organic compounds, particularly in the oxidative cleavage of double bonds, making it a key tool in the pharmaceutical and chemical industriesBatteries: Manganato compounds are used in certain types of batteries, like lithium-ion batteries, where they contribute to the cell’s overall performance
Environmental Remediation: Manganato can be used in environmental remediation efforts to treat and eliminate pollutants, such as chlorinated solvents, in soil and groundwater Manganato-based catalysts are employed in various chemical reactions, accelerating the transformation of reactants into desired products, making chemical processes more efficient.
Conclusion
Manganato, with its distinctive structure and remarkable properties, has earned its place as a versatile compound with significant applications in various fields. Its presence can be felt in analytical laboratories, water treatment facilities, organic synthesis laboratories, and even in the batteries that power our devices. As we continue to explore the world of chemistry, manganato stands as a testament to the boundless potential of chemical compounds and their capacity to shape the world around us. Whether in a laboratory or an industrial setting, manganato’s versatility ensures that it will remain a powerful and essential tool in the world of science and technology.