Ozempic: A Multifaceted Injection for Type 2 Diabetes and Beyond

Ozempic, a brand name for the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist semaglutide, has become a prominent player in the management of type 2 diabetes. But its potential goes beyond simply regulating blood sugar. This article delves into the multifaceted nature of Ozempic, exploring its uses, mechanisms, benefits, potential side effects, and ongoing research.
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes:
Before diving into Ozempic, understanding the disease it targets is crucial. Type 2 diabetes arises when the body struggles to regulate blood sugar (glucose) levels effectively. This can occur due to insufficient insulin production or resistance to its effects. Over time, uncontrolled blood sugar can lead to serious complications like heart disease, stroke, and nerve damage.
Ozempic: Mimicking the Gut Hormone:
Ozempic mimics the action of a naturally occurring gut hormone called GLP-1, which plays a crucial role in blood sugar control. GLP-1 slows stomach emptying, promotes insulin release, and reduces glucagon secretion (a hormone that raises blood sugar). By mimicking these effects, Ozempic helps regulate blood sugar levels in several ways:
- Increased Insulin Release: Ozempic stimulates the pancreas to release more insulin, especially after meals, when blood sugar levels naturally rise.
- Reduced Glucagon Secretion: Ozempic suppresses the release of glucagon from the pancreas, preventing excessive sugar production by the liver.
- Delayed Stomach Emptying: Ozempic slows down the rate at which food exits the stomach, leading to a more gradual rise in blood sugar after meals.
Beyond Blood Sugar: The Weight Loss Factor:
Ozempic, interestingly, has shown significant potential for weight loss. While not officially approved for this purpose, studies have demonstrated an average weight loss of 5-10% in individuals with type 2 diabetes using Ozempic. This effect is attributed to multiple mechanisms, including:
- Reduced Appetite: The drug can influence appetite-regulating hormones, leading to feelings of fullness and reduced calorie intake.
- Increased Energy Expenditure: Ozempic may slightly boost metabolism, potentially increasing calorie burning.
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Enhanced insulin sensitivity promotes fat storage in muscles instead of visceral fat, contributing to weight loss.
Current Uses and Future Applications:
Currently, Ozempic is approved for:
- Treating type 2 diabetes: Used alongside diet and exercise, it helps manage blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications in adults.
- Reducing cardiovascular risk: In individuals with type 2 diabetes and established heart disease, Ozempic has shown to lower the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events.
Research is actively exploring Ozempic’s potential in other areas, including:
- Treating obesity: Ongoing clinical trials assess its efficacy in managing weight and its associated health risks in non-diabetic individuals.
- Prediabetes management: Investigating its ability to prevent or delay the progression of prediabetes to full-blown diabetes.
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): Exploring its potential to improve liver health in individuals with NAFLD.
Weighing the Benefits and Risks:
While Ozempic offers promising benefits, potential side effects require consideration:
- Gastrointestinal side effects: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation are common, usually mild and transient.
- Gallbladder problems: In rare cases, Ozempic may increase the risk of gallstones or pancreatitis.
- Allergic reactions: Serious allergic reactions are rare but possible.
- Low blood sugar: Ozempic can lower blood sugar levels, so careful monitoring and medication adjustments may be needed.
Ozempic: A Personalized Approach is Key
Ozempic represents a significant advancement in diabetes management, offering potential benefits beyond blood sugar control. However, it’s crucial to remember that its use should be individualized and closely monitored by healthcare professionals. Discussing your specific needs and potential risks with your doctor is essential before embarking on the Ozempic journey.
Additional Considerations:
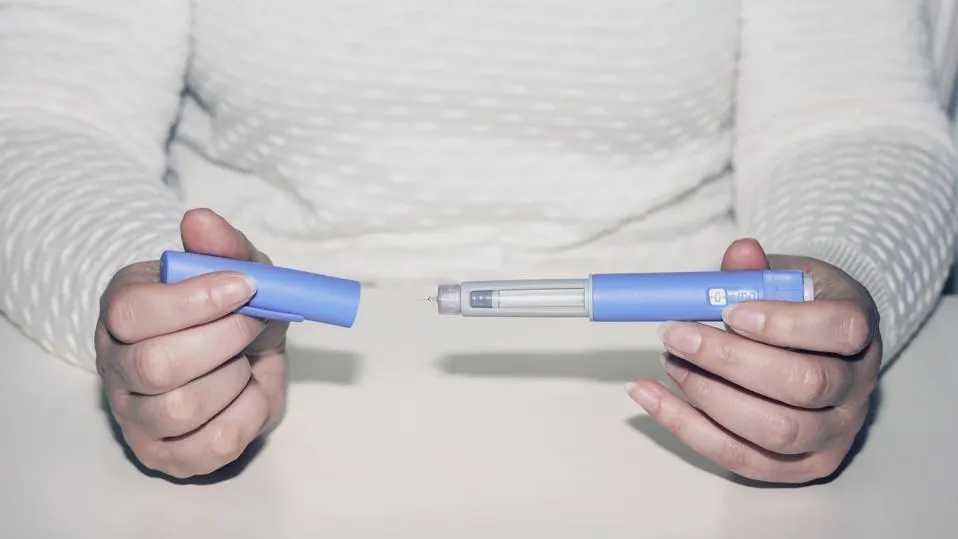
- Ozempic is injected weekly, requiring commitment and proper administration techniques.
- The medication is not a cure for type 2 diabetes and should be used alongside lifestyle modifications, including healthy diet and exercise.
- The long-term effects and safety profile of Ozempic are still under investigation, and ongoing research is crucial.
Conclusion:
Ozempic offers a promising approach to managing type 2 diabetes and potentially impacting other health conditions. By understanding its mechanisms, benefits, and potential side effects, individuals can engage in informed discussions with their healthcare providers to determine if this innovative injection could be a valuable addition to their personalized treatment plan. Remember, individual needs and circumstances vary greatly, so seeking professional guidance is crucial for navigating the world of diabetes management effectively