Navigating the Upside Down: A Deep Dive into the Trendelenburg Position
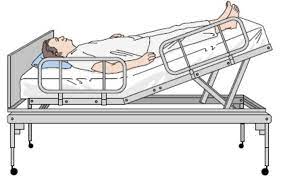
Imagine yourself lying flat on your back, but with your feet magically hoisted higher than your head. This gravity-defying posture isn’t a scene from a sci-fi movie, but the Trendelenburg position, a medical maneuver with a rich history and diverse applications. Named after German surgeon Friedrich Trendelenburg who popularized it in the late 19th century, this incline has become a mainstay in operating rooms and beyond.
Head Down, Feet Up: Unveiling the Trendelenburg Angle
The Trendelenburg position isn’t a one-size-fits-all affair. The incline of the patient’s body can range from a gentle 15 degrees to a steeper 30 degrees, depending on the intended purpose. This tilt, achieved by adjusting the operating table or bed, brings about a cascade of physiological changes within the body.
Firstly, blood, responding to gravity’s pull, shifts downwards, pooling in the legs and abdomen. This redistribution can be beneficial in several ways:
- Enhanced surgical access: In abdominal and pelvic surgeries, pooling blood away from the operative field improves visibility and facilitates the surgeon’s work.
- Improved venous return: For patients in shock or with congestive heart failure, the Trendelenburg position can increase venous return to the heart, boosting its pumping efficiency and improving blood flow to vital organs.
- Cerebral protection: During neurosurgery, lowering the head relative to the body can reduce pressure within the skull, protecting the delicate brain tissue.
Beyond the Operating Room: Trendelenburg’s Wider Reach
While surgery takes center stage, the Trendelenburg position finds applications in other medical settings as well:
- Critical care: For patients with severe respiratory distress, a modified Trendelenburg position with a slight head and chest elevation can improve lung function and breathing.
- Imaging: In X-rays and CT scans of the abdomen, the Trendelenburg position can help differentiate fluid from bowel loops, aiding in diagnosis.
- Central venous catheterization: Placing catheters in large veins near the heart becomes easier with the Trendelenburg position, as the veins become fuller and easier to access.
Not All Uphill Battles are Easy: Potential Drawbacks
It’s important to remember that no medical intervention is without its potential downsides. The Trendelenburg position is no exception. Some possible concerns include:
- Increased venous pressure in the legs: This can lead to blood clots in susceptible individuals.
- Decreased cerebral blood flow: In patients with compromised circulation, the head-down tilt can worsen brain perfusion.
- Eye pressure: The Trendelenburg position can elevate eye pressure, potentially posing a risk for glaucoma patients.
Therefore, careful patient selection and meticulous monitoring of vital signs are crucial when employing the Trendelenburg position.
A Balancing Act: Modified Trendelenburg and Reverse Trendelenburg
The Trendelenburg position isn’t a lone wolf in the realm of body tilt. Two close relatives share the spotlight:
- Modified Trendelenburg: This variation involves raising the head and chest slightly while maintaining the feet-higher-than-head position. This addresses concerns about decreased cerebral blood flow while still providing some of the benefits of the classic Trendelenburg.
- Reverse Trendelenburg: As the name suggests, this position flips the script, tilting the patient head-up with the feet lower. This is primarily used in neurosurgery to improve drainage of cerebrospinal fluid and reduce intracranial pressure.
From History Books to Cutting Edge: The Trendelenburg Legacy
The Trendelenburg position’s journey through medical history is fascinating. Initially used for shock management, it evolved into a surgical workhorse and diversified its applications across various medical specialties. Today, research continues to explore the nuances of the Trendelenburg position, investigating its effectiveness in specific procedures and optimizing its safety profile.
Beyond the Technical: Humanizing the Trendelenburg Experience
For patients, the Trendelenburg position can be a disorienting and even unsettling experience. Understanding the rationale behind the tilt and potential concerns can ease anxieties. Open communication with medical staff and ensuring comfort through proper padding and positioning are crucial to making the journey through this upside-down world a smooth one.
In Conclusion: A Multifaceted Maneuver with Enduring Relevance
The Trendelenburg position is a testament to the power of simple yet ingenious medical interventions. Its ability to manipulate gravity for therapeutic benefit continues to inspire and innovate. As we delve deeper into understanding its mechanisms and refine its applications, the Trendelenburg position promises to remain a valuable tool in the medical arsenal, helping countless patients navigate their own uphill battles towards recovery.